Cat and kitten vaccination schedule & cat vaccination costs

Summary
Kittens need a series of core vaccinations over several visits, with non-core vaccines based on risk and lifestyle. Kitten vaccinations are followed by adult boosters. This article outlines typical Australian costs per visit, what each vaccine protects against and what to expect at your appointment. Keep a record of dates, discuss local disease risks with your vet and maintain boosters so your cat stays protected throughout life.
The importance of cat and kitten vaccination
Getting your cat or kitten vaccinated can protect them from being susceptible to viral infections making them seriously sick. Cat vaccinations are not only a cost-effective way to protect your beloved family member, but can also help you avoid the stress of having a seriously ill pet and the high cost of veterinary treatment that accompanies severe illness.
A range of cat vaccinations are available to help protect your cat from debilitating diseases. In this article we discuss everything you need to know about feline vaccinations, vaccination costs, the recommended vaccination schedule, and potential cat vaccination side effects.
What are cat vaccines and how do they work?
Vaccines for cats and kittens operate in the same way as they do for humans. Vaccines are health products that trigger the body’s immune system to fight a particular infectious agent, without causing the actual illness or disease. In most cases, the germs in the vaccine are weak or dead. Some vaccines don’t even contain any of the germs; rather, they simply mimic them.
Vaccinations are designed to stimulate and train your cat’s immune system. After receiving the vaccine, the white blood cells in your cat’s body produce proteins (antibodies) that will, together with other white blood cells, fight the infectious agent (antigens).
It is important to understand that most vaccines work by preventing your cat from becoming sick. While being vaccinated will prevent your cat from showing symptoms of the disease, it may not necessarily protect the cat from the infection. However, the infection will be less severe if they do get it as their immune system is primed to take action.
Expert advice from Dr Felicia:
Since cat vaccinations are given under the skin rather than into the muscle, injections are less painful than what we typically experience when we receive vaccinations.
Which are the most common cat and kitten vaccinations?
The Australian Veterinary Association (AVA) categorises recommended cat vaccinations into “core” and “non-core” vaccines.
Core vaccines
Core vaccines are those on the cat vaccination schedule that are appropriate for cats regardless of where they live. In Australia, there are three core cat vaccines, which together are called the F3 vaccination:
- Feline herpes virus
- Feline calicivirus
- Feline parvovirus / feline panleukopoenia
Non-core vaccines
There are non-core vaccines available for certain other diseases which may be recommend based where the cat lives and its individual lifestyle. These should be discussed with the veterinarian on a case-by-case basis.
Non-core cat vaccinations include vaccinations against the following diseases:
- Feline leukaemia virus (FeLV)
- Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)
- Chlamydia felis
- Bordetella bronchiseptica
What are F3, F5 and F6 vaccinations?
Cat vaccinations are typically administered in combination, rather than individually. The terms F3, F5 and F6 refer to how many diseases your cat will be vaccinated against.
The F3 Vaccine – Feline 3 (F3) – covers three major diseases:
- Feline herpes virus, which is also called viral rhinotracheitis or simply cat flu. This disease occurs commonly in unvaccinated cats. Typical symptoms are nasal discharge, red eyes and gum infections. It can also cause long-term problems like chronic sneezing.
- Feline calicivirus, which is another virus that can cause the disease more commonly known as cat flu.
- Feline panleukopaenia, also know as cat parvovirus or feline enteritis, can cause severe, and sometimes fatal, gastroenteritis.
The F5 cat vaccination offers protection against feline herpes, calcivirus and panleukopaenia, along with additional protection against feline chlamydia and feline leukaemia.
The F6 vaccination immunises against all of the diseases included in the F5 vaccine along with the feline immunodeficiency virus (Feline AIDS).
The following diagram summarises the various diseases and which vaccinations cover them:
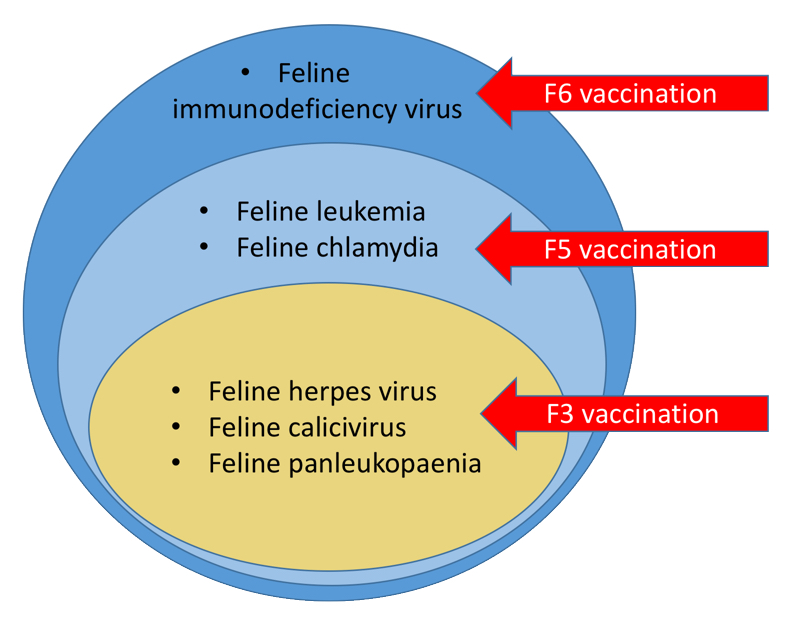
Cat and kitten diseases that can be vaccinated against
Feline Panleukopaenia or Feline Enteritis or Cat Parvovirus
Feline panleukopaenia, also known as feline enteritis or cat parvovirus, is a very contagious disease spread easily through body secretions and via objects such as bedding, litter trays, food bowls. It is most common in young, unvaccinated cats and cats in group housing. Prognosis is poor for affected cats. Vaccines against feline parvovirus are very effective, with vaccinated cats completely protected from clinical disease.
Feline herpes virus & calicivirus – Feline respiratory diseases
Also known as cat flu, two common feline respiratory diseases are the feline herpes virus and feline calicivirus. Symptoms of these infections include nasal discharge, watery eyes, sneezing and coughing. These respiratory diseases are generally not fatal but can cause distress for the infected cat. They can occur in cats and kittens of any age, are highly contagious, and even after symptoms resolve, cats can still be ‘carriers’ and continue to spread the infection.

Feline Herpes Virus
This disease is marked by fever, which can come and go, as well as sneezing and inflamed eyes. Often there is discharge from the nose and eyes containing mucus and pus which starts off clear and thickens with the progression of the illness. Some cats develop mouth sores and loss of appetite because of the resultant discomfort when eating; weight loss is another common side effect for these cats.
Feline Calicivirus
Although the feline calicivirus typically causes few or no signs, in some cats it can develop to pneumonia from fluid build-up in the lungs. It is often impossible to distinguish feline herpesvirus from feline calicivirus infections as the symptoms are so similar.
Feline Leukaemia Virus
Cats can transmit this virus through almost any body fluid, including saliva, tears, urine and even faeces. They can be infected with this virus from being bitten by another cat. Transmission can also occur from sharing food and water dishes, and litter trays.
An infected cat or kitten will show signs of low to no appetite, which generally results in weight loss and subsequent anaemia. Some cats will also experience vomiting and diarrhoea. Over time the immune system may become so impaired that the cat may become anemic, be more susceptible to tumours or develop neurological signs.
A blood test can detect if a cat has contracted Feline Leukemia Virus, but sadly there is currently no treatment available, only management of the condition until cancer develops. Cats considered high risk (eg. Living with FeLV-infected cats or in group housing/shelters) should be vaccinated for FeLV.
Feline Chlamydophila
Chlamydia felis is the bacteria responsible for feline Chlamydophila, a respiratory disease, but with the most common finding of conjunctivitis or pink eye in cats (i.e. inflammation of the eye tissue). It is highly contagious and spread through contact with eye secretions, with outbreaks most commonly occurring in shelters and catteries. Vaccination reduces clinical signs but does not prevent colonisation of the conjunctiva, and is recommended only for cats in high-risk environments (eg. Overcrowded shelters with multiple confirmed cases).
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus or Feline Aids
This virus is spread between cats through biting and fighting. Infections cause immune suppression which occurs in stages, with the later stages seeing cats more susceptible to infections, immune-mediated diseases, cancers and suppression of the bone marrow.
Vaccination against FIV is considered non-core, with effectiveness of the vaccine around 50%. Vaccination against FIV is considered optional for individually housed cats.
Summary of cat diseases that can be vaccinated against
|
Disease Name |
Risks |
Vaccines |
|---|---|---|
|
Feline Herpes virus |
Highly contagious; can cause weight loss & distress for cat | F3 |
|
Feline Calicivirus |
Fluid build-up can lead to pneumonia | F3 |
| Feline Panleukopoenia | Rapid progression; highly contagious; can be fatal | F3 F5 F6 |
| Feline Leukaemia Virus (FeLV) | Anaemia; development of untreatable cancer | F5 F6 |
| Feline Chlamydia | Lung infection in young kittens | F5 F6 |
| Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) | Highly contagious; can be fatal if not treated in time | F6 |
Kitten vaccination guidelines
Young kittens receive antibodies from their mother’s milk and are therefore protected to some extent in their early stages of life. Over time, the maternal antibodies reduce, and correspondingly, the protection these provide against diseases.
To ensure ongoing protection for your kitten’s first year of life, it is recommended to get the first vaccination from as early as 8 weeks of age. A booster (2nd vaccination) is recommended four weeks after the first vaccination and a further booster (3rd vaccination) should follow four weeks after the second. A kitten can safely go outside ten days after getting its final kitten vaccination.
Your kitten’s second and third vaccinations, or boosters, are necessary because the maternal antibodies decline over the first couple of months; however, until these levels drop sufficiently they can also neutralise the early vaccines given. This is why a series of vaccinations is required to ensure sufficient protection.
To maintain immunity after your kitten has received the three initial vaccinations, further boosters will be required annually, or in some cases, every three years. Please let your vet advise you on required vaccination frequency, as this depends on your cat’s individual needs and lifestyle.
Below are some rough guidelines as to what age your kitten should be when receiving its various vaccinations:
|
Disease name |
Age at vaccination |
Vaccines |
|---|---|---|
| Feline Herpesvirus
Feline Calicivirus Feline Panleukopenia |
>6 weeks of age, |
F3 F5 F6 |
| Feline Chlamydia |
>9weeks of age, |
F5 F6 |
| Feline Leukaemia Virus (FeLV) |
>8-12 weeks of age |
F5 F6 |
| Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) | >9 weeks of age, two doses should be given 2-3 weeks apart |
F6 |
It is also worth noting that microchipping a kitten or cat is mandatory in NSW and some other states in Australia. It is the simplest way ensure that your precious new family member can be identified and traced if he gets lost. If the breeder to shelter hasn’t already microchipped your kitten, we recommend asking your vet to do so at your first visit.
Expert advice from Dr Felicia:
Some cats really struggle with being placed in a carrier and then transported to the vet in the car, and may show signs of stress by becoming aggressive at the clinic. For these patients some clinics will suggest some medication to be given just prior to the visit to help take the edge off for your cat. Another option may be looking into vets that perform house calls to reduce the amount of stress for both of you.
Vaccination side effects
Vaccinations help prevent your kitten from catching some nasty and potentially life-threatening diseases, but you should be aware that vaccinations can potentially cause some minor and extremely rare side effects.

Here are some side effects your cat or kitten can experience after receiving their vaccinations:
- Lack of appetite
- Increase in body temperature
- Lethargy
- Skin irritation and/or bruising around the injection area
- Allergic reaction to the vaccine causing vomiting, diarrhoea and shortness of breath
The side effects will usually present themselves shortly after the vaccine has been given, not hours or days later. It is important to stay at the vet for a short time after each vaccination so that the vet can check that your cat does not show any signs of an allergic reaction.
Because it is difficult to predict the costs of veterinary care, it can help to have measures in place to help prepare for the unexpected. Pet insurance can help by covering a portion of the eligible vet bill if the unexpected does happen.
Get a quick quote
Cat vaccination aftercare
Some kittens and cats will seem a bit more needy and may seek comfort and privacy after their vaccinations, while others will jump around like nothing has happened. Don’t be alarmed if she doesn’t eat anything or wants to be left alone for the first 24 hours. After that your cat should be back to its usual self.
Here are some tips for caring for your cat following his or her vaccinations:
- Provide your cat with a warm and quiet place to rest
- Make sure she has access to water and her favourite food
- Avoid touching or patting the area where she received the injection, as it may a be a bit sore at the site
- Avoid rough play for the first couple of days
- Check up on her regularly to ensure she is comfortable and isn’t showing any side effects
Average cost of cat vaccinations
The cost for cat and kitten vaccinations can vary considerably depending on the type of vaccine and your location. However, as a rough guide, cat vaccinations in Australia are usually in the range of $80 to $150 each. We suggest you check with your local vet clinic to find out their specific vaccination prices.
Is the cost of vaccination worth it? Bear in mind that if your kitten or cat needs to be hospitalised a a result of catching a life threatening disease, the cost for treatment can run into the thousands. Vaccination helps saves lives and prevents the grief and expenses associated with your cat catching a nasty illness.
Bow Wow Meow gives you the option to add on Routine Care (non-insurance benefit), which provides a contribution towards everyday items such as vaccinations, de-sexing and health checks.
Learn more about our Routine Care (non-insurance benefit).
Do indoor cats need to be vaccinated?
If you have an indoor cat that doesn’t have any contact with other cats or animals outside your house, you should discuss with your vet if all the usual cat vaccinations will be required.
Certain diseases, like Feline Respiratory Disease and Feline Enteritis, can only be contracted from other cats. While these two diseases might not be an issue for your indoor cat, if you are planning to take your cat to boarding or even to the vet where other sick cats have been, she might still be at risk.
Worried about over-vaccinating? Titre testing may be an option…
Over the last decade there has been increasing debate concerning the over-vaccination of pets. One argument is that depending on the vaccine, immunity can last significantly longer than twelve months. Some pet owners therefore worry about vaccinating their cats while they still have immunity from the previous time.
If you are concerned, you can talk to your vet about titre testing, which tests the levels of remaining antibodies in your cat’s blood. To check these remaining levels, a small blood sample is taken and send to a laboratory. If antibody levels are shown to be sufficient, you can delay the vaccinations; if not, you will need to vaccinate your cat.
In conclusion
While you may wonder if immunisation is really necessary or you may find it costly, it is an essential part of ensuring your cat lives a happy and healthy life.
There are a range of different levels and types of vaccines available, and not all may be necessary for your cat. Always speak to your vet who will consider your cat’s location and lifestyle when providing the recommended schedule for your individual cat.
Remember, whilst immunisations can never be 100% effective, they are a highly effective way of preventing the stress, heartache and cost of your cat contracting a major disease. Seeking out pet insurance is a great way to help cover these costs. Bow Wow Meow gives you the option to add on Routine Care (non-insurance benefit), which provides a contribution towards everyday items such as vaccinations, de-sexing and health checks.
Bow Wow Meow Pet Insurance can help protect you and your cat should an unexpected trip to the vet occur.
-
Find out more about our cat insurance options
-
Get an online pet insurance quote
Bow Wow Meow is proud to have been awarded winner of Canstar’s ‘Most Satisfied Customers’ Award in the Pet Insurance category for both 2024 and 2025!
Bow Wow Meow is proud to have been chosen as Product Review’s Pet Insurance Award Winner every year from 2018 to 2025! This is based on 2,995 independent customer reviews (as at 21/01/2025), with an overall rating of 4.3*
Google Review rating = 4.5* (based on 968 reviews)
Trust Pilot rating = 4.6* (based on 531 reviews)
Bow Wow Meow is proud to have been chosen as Product Review’s Pet Insurance Award Winner every year from 2018 to 2025! This is based on 2,995 independent customer reviews (as at 21/01/2025), with an overall rating of 4.3*
Google Review rating = 4.5* (based on 968 reviews)
Trust Pilot rating = 4.6* (based on 531 reviews)
Bow Wow Meow has been chosen as a winner in the Finder Pet Insurance Awards 2024. Finder’s panel of experts analysed over 140 quotes to award our Ultimate Care Plan the winner of the “Pet Insurance – Value” category.